Part 1: Datalad basics
Install datalad
Install datalad in which ever way is possible. Look at
pip3 install datalad-installer
datalad-installer
how this is possible the easiest. On fedora, you can use
dnf install datalad
on Ubuntu, you can use
apt install git git-annex
pip3 install datalad
Create a new dataset
We have data, that someone produced (maybe it was us, maybe it was one of our collaborators) and we only need to analyse it. Practically, this data is already published as a Datalad dataset, that we will download in just a moment. To speed things up a little, I have already made a python script for you to try and analyse this.
For our analysis, we want to make a new dataset, in which we import the raw data and analyse it with a python script.
datalad create analysis
cd analysis
Add content
Imagine you already have some kind of script, that you have written. An already prepared example can be downloaded from here:
wget -O script.py https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jkuhl-uni/datalad-code-along/master/src/files/script.py
By downloading it, we have changed something in a DataLad-tracked folder. Analogous to a git-repository, we commit the changes:
datalad save -m "add analysis script"
The analysis script is to be used as
python3 ./script.py <data-file> <output-file>
Add another dataset
Next, we want to download the data, that we want to analyse:
datalad install https://github.com/jkuhl-uni/test-data.git
datalad save -m "add data as sub-dataset"
Run the analysis script
Let's try to run it with the first data file:
python3 ./script.py test-data/data1.out ./plot1.pdf
We find that this does not work. This is, since we only have the place-holder files in our installation of the data dataset.
we run
datalad get test-data/data1.out
to retrieve the data. Then we run the script again:
python3 ./script.py test-data/data1.out ./plot1.pdf
Now it works!
We can have a look at the plot. it should look something like this:
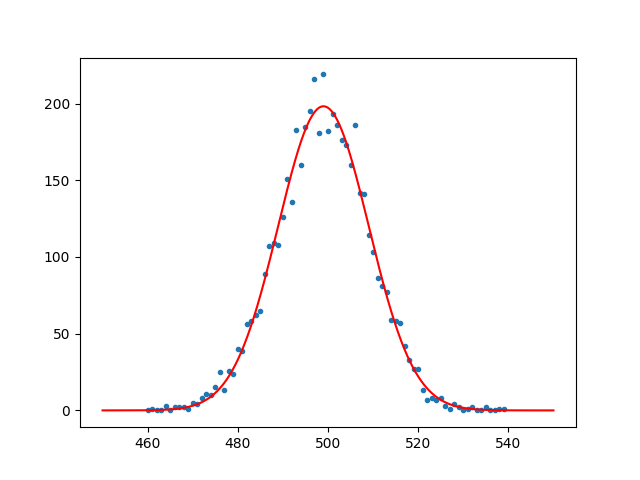
we have changed the dataset analysis. So datalad should also include these changes:
datalad save -m "add a first plot"
Cool, we have a new file in the dataset. But people won't know, how we did this.
Use datalad run and datalad rerun
Instead, we can use datalad run to make this more reproducible.
datalad run -i script.py -i test-data/data2.out -o plot2.pdf -m "add a second plot with datalad run" "python3 ./script.py test-data/data2.out plot2.pdf"
Nice, this looks pretty easy.
We can have a look at the history of the repository as usual with git log [--oneline].
Alright. Now imagine we just had a stroke and forgot how the heck we got the second plot. Luckily, we ran this with datalad run. To redo the changes applied with this commit, we run
datalad rerun <last-commit-id>
to re-do the plot we just made.